Resource allocation means assigning the right people, tools, and budget at the right time so projects finish on schedule and teams stay healthy. When treated as a strategic function, allocation turns plans into realistic roadmaps that reduce delays and prevent burnout.
September 15, 2025 (5mo ago) — last updated December 21, 2025 (1mo ago)
Resource Allocation for Project Success
Expert techniques to plan, track, and optimize people, tools, and budgets for better project outcomes and less burnout.
← Back to blog
Mastering Resource Allocation Project Management
Summary
Discover expert techniques to plan, track, and optimize people, tools, and budgets for better project outcomes and less burnout.
Introduction
Resource allocation in project management means assigning the right people, equipment, and budget at the right time so projects finish on schedule and teams stay healthy. When you treat resource allocation as a strategic function—not just an administrative task—you transform a static plan into a realistic, executable roadmap that prevents burnout, reduces delays, and improves delivery quality.
Why Resource Allocation Is Your Project’s Secret Weapon

Smart resource allocation connects project goals to daily work. Without it, even brilliant plans can falter under missed deadlines and rising costs. Treating resource management as strategic lets you make deliberate choices that boost efficiency, reduce risk, and keep your team motivated.
The Strategic Importance of Allocation
When you get allocation right, you avoid two common killers: overallocation and underutilization. Overallocation piles work onto individuals and drives burnout. Underutilization wastes talent and budget and increases disengagement. A coordinated approach scales with more initiatives and a growing portfolio; the project portfolio management market is expanding rapidly, reflecting this need1. Many project managers juggle multiple projects at once, so efficient resource distribution is essential for survival2.
Clarifying Key Concepts
Resource allocation assigns resources. Resource leveling and smoothing optimize those assignments when constraints appear. Think of allocation as the initial plan; leveling and smoothing are tactical adjustments when reality shifts.
Key Resource Allocation Concepts at a Glance
| Concept | Primary Goal | When to Use It |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Allocation | Assign and schedule people, equipment, and budget to tasks. | During initial project planning to set the baseline. |
| Resource Leveling | Resolve overallocation by adjusting schedules (may extend timeline). | When a team member has more work than they can handle. |
| Resource Smoothing | Balance workloads without changing the deadline. | When deadlines are fixed and you must optimize within float. |
Building Your Resource Management Plan

A resource management plan is your project’s living blueprint. It answers: What do we need? When do we need it? Who’s doing what? Creating a single source of truth prevents last-minute scrambles that sink timelines and budgets.
Identifying and Categorizing Your Resources
Inventory everything your project needs, not just people. Break resources into categories:
- Human resources — skills, experience level, and availability.
- Equipment — machinery, testing devices, laptops.
- Software and technology — licenses, cloud services, platforms.
- Facilities — office space, labs, meeting rooms.
- Financial resources — the project budget and contingency.
A broad inventory prevents surprises like expired licenses or double-booked labs derailing work.
Forecasting and Predicting Resource Demand
Estimate how much of each resource you’ll need and for how long. Use bottom-up estimating for detailed tasks (sum task hours for developer work) and analogous estimating for repeatable work like marketing campaigns. These methods turn your inventory into a time-based schedule of demand.
Visualizing Your Plan With Practical Tools
Use visual tools to make the plan actionable:
- Skills matrix — maps people to skills and reveals gaps.
- Resource calendar — shows availability across the timeline and avoids conflicts.
- Gantt chart — assigns resources to tasks so you can see who’s working on what and when.
These tools become your live dashboard for monitoring and adjustments. Many organizations name improving resource allocation a top priority, yet a smaller share invest in advanced tooling to do it well3.
Proven Techniques for Smart Resource Allocation
Once your plan exists, apply methods that make allocation dynamic and resilient. These practical techniques help resolve overallocation and adapt to shifting priorities.
Using Resource Leveling to Prevent Burnout
Resource leveling resolves conflicts when someone is overallocated. It fixes daily or weekly overages by shifting tasks, which may extend the timeline but preserves quality and team well-being. Leveling is an important trade-off: a minor schedule change now avoids costly errors and burnout later.
Optimizing With Resource Smoothing
Resource smoothing optimizes workloads without changing the project’s critical path. Move noncritical tasks within their float so workloads are steadier while keeping deadlines intact. Smoothing is ideal for projects with immovable deadlines.
Comparing Resource Leveling and Resource Smoothing
| Technique | Primary Objective | Impact on Timeline | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource Leveling | Resolve overallocation | May extend deadline | Flexible-timeline projects prioritizing team health |
| Resource Smoothing | Balance workload within schedule | No change to deadline | Fixed-deadline projects that can’t slip |
Making Tough Decisions With Prioritization Frameworks
When resources are constrained, use a prioritization framework such as MoSCoW:
- Must-Have — essential tasks first.
- Should-Have — important but not critical.
- Could-Have — desirable if time allows.
- Won’t-Have (This Time) — out of scope for the phase.
Frameworks force clear discussions with stakeholders so resources target highest-impact work.
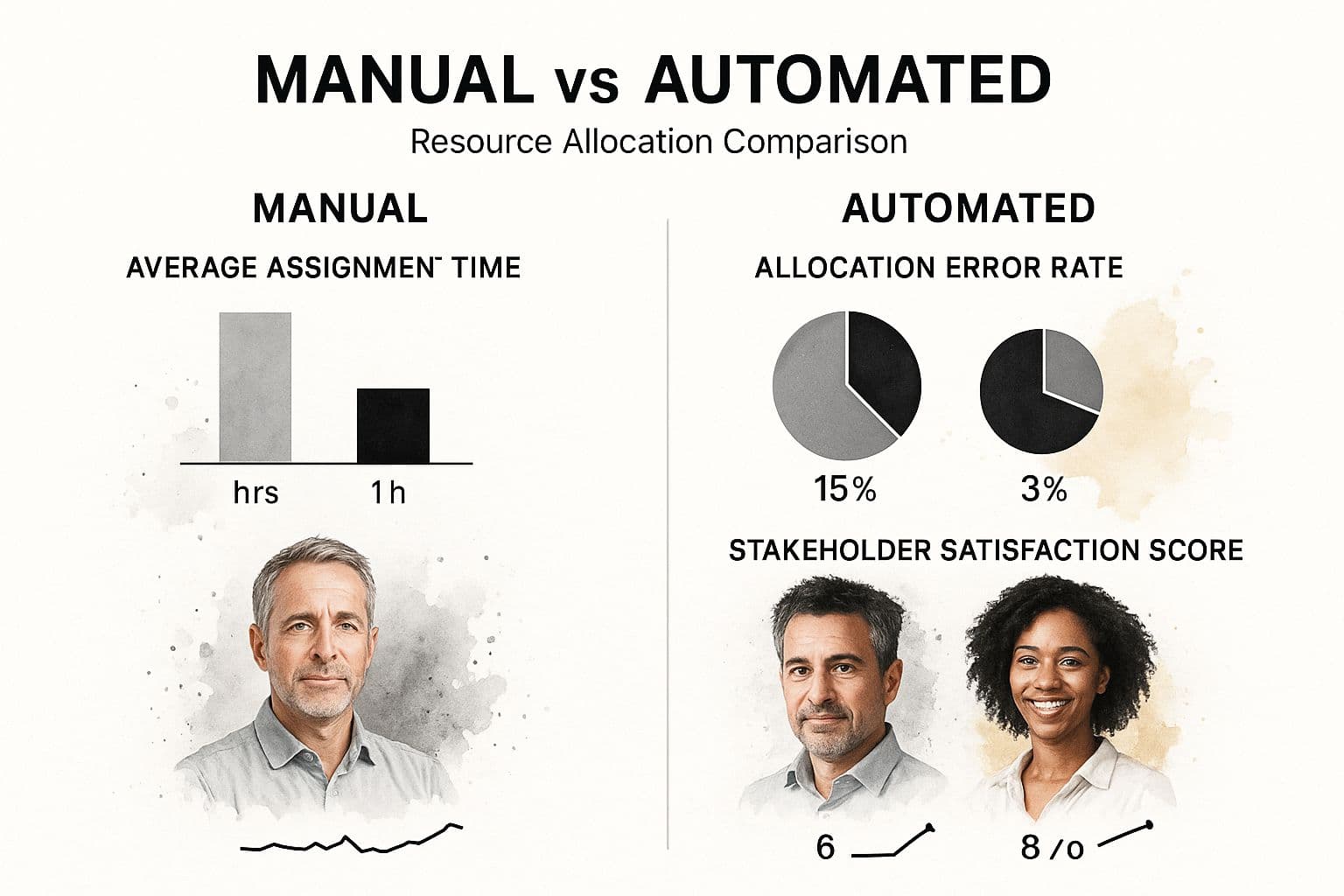
Automation can dramatically reduce assignment time and errors, improving stakeholder satisfaction. For practical automation strategies, see our guide to automated project management on Fluidwave’s blog.
How to Monitor and Optimize Resource Use

Your plan is the map; monitoring is the GPS. Regular tracking and timely adjustments turn a static plan into a responsive strategy that navigates unexpected changes.
Key Metrics for Resource Monitoring
Track a short set of KPIs as an early-warning system:
- Planned vs. actual hours — reveals where estimates diverge from reality.
- Resource utilization rate — shows how much of someone’s available time is used; sustained 100% is a burnout risk, while very low rates indicate underuse.
- Budget variance — flags cost overruns early so you can reallocate funds or adjust scope.
Review these regularly to stay ahead of problems and course-correct before they escalate.
Running Effective Resource Review Meetings
Hold regular, structured resource review meetings that focus on forward-looking allocation and conflict avoidance. Bring the right people together, review capacity for upcoming work, and make proactive reallocations.
A Framework for Proactive Reallocation
When scope or priorities change, follow a simple process:
- Assess the impact — estimate hours and which tasks or people are affected.
- Communicate with stakeholders — present the trade-offs clearly.
- Renegotiate and reprioritize — document what changes and why.
This reduces scrambling and turns changes into deliberate decisions.
Navigating Common Resource Allocation Hurdles
Projects are messy; priorities shift and new requests arrive. Understand the common pitfalls so your plan survives the real world.
The True Cost of Misallocation
Overallocation increases mistakes and burnout; underutilization increases attrition and wastes budget. Poor resource allocation is linked to a significant share of project delays and quality problems, and many organizations still lack consistent resource-management practices4.
Defending Your Plan Against Scope Creep
Treat your resource plan like a fortress. For any new request, run a quick impact analysis:
- What’s the real effort in hours?
- Which tasks get delayed?
- What are the trade-offs in people and budget?
Present stakeholders with clear choices so additions become strategic decisions, not hidden scope creep. For a deeper guide, see Fluidwave’s article on managing scope creep.
Negotiating for Shared Resources
When resources are shared across teams, bring data to the negotiation. Show the cost of not having the resource and propose creative alternatives like partial oversight or using a junior team member with expert checkpoints. Framing the ask as risk mitigation, not a favor, improves outcomes.
Your Top Resource Allocation Questions, Answered
What’s the very first thing I should do when allocating resources?
After completing the work breakdown structure (WBS), build a resource breakdown structure (RBS). The RBS catalogs every skill, piece of equipment, software license, and space you’ll need so you can match tasks to the right resources before assignments begin.
How do I handle it when a key person suddenly isn’t available?
Gauge the impact on the critical path, communicate immediately with stakeholders, and deploy your contingency plan: a preidentified backup, cross-trained team members, or a temporary loan from another department.
What’s a realistic resource utilization rate to aim for?
Target around 80–85% utilization. That buffer isn’t slack; it’s time for administrative work, meetings, learning, and handling urgent requests without breaking the schedule5.
Ready to stop guessing and start optimizing your team’s workload? Fluidwave provides AI-driven clarity to balance tasks, prevent burnout, and hit deadlines. Visualize workloads, automate assignments, and delegate to skilled virtual assistants in one place at https://fluidwave.com.
Focus on What Matters.
Experience lightning-fast task management with AI-powered workflows. Our automation helps busy professionals save 4+ hours weekly.